The New Rebirth of Syria Sets Sail
By Ikuzo Kobayashi, President of the NPO Salaam Association
From the Summer Issue of the electronic “Salaam Quarterly Bulletin”, No.55, Nov 2025
Introduction

Al-Jolani, leader of the opposition forces, speaks at a mosque in central Damascus on Dec. 8. Screenshot and caption from BBC News Japan, Dec. 9, 2024.
Since the onset of the Arab Spring in late 2010, Syria has endured fourteen years of civil war. Then, on December 8 of last year, the Assad regime suddenly collapsed, bringing the long and brutal conflict to an end. Ironically, this was due to Israel. The chain of events that ended the war began when Hezbollah, the Lebanese non-governmental military organization supporting Assad, was driven to destruction by Israel, a nation long hostile to Syria.
Let us look more closely at this development. In 2014, when the Assad regime was on the brink of collapse after losing 60% of its territory to ISIL (the so-called Islamic State), it was revived by Russian airstrikes. The regime’s survival also depended heavily on Shiite militias under the command of Iran’s Revolutionary Guard Corps and on Hezbollah fighters who had entered from Lebanon. Then came the Gaza War in October 2023. In exercising its right to self-defense, Israel launched airstrikes against Hezbollah and senior figures in Iran’s Revolutionary Guard Corps who were supporting Hamas, driving both forces to near annihilation.
A ceasefire agreement between Israel and Lebanon was reached on November 27, 2024. Soon afterward, nti-government forces in northwestern Syria’s Idlib Province—namely the Islamist group Hay’at Tahrir al-Sham (HTS)—launched an offensive against Syrian government troops. By November 30, they had seized Aleppo. Although Russia conducted sporadic airstrikes, there was no meaningful support for the Assad regime, nor did Iran provide substantial reinforcement.
By December 2, the HTS-led opposition forces had advanced to Hama, reached Homs by the 5th, and entered Damascus on the 8th—toppling the Assad regime. It all happened in the blink of an eye.
The leading opposition group, Hay’at Tahrir al-Sham (HTS), was formed in January 2017. Its leader, Abu Mohammad al-Julani, had previously commanded the al-Qaeda-affiliated al-Nusra Front. However, he broke with IS in 2014 and announced a severance from al-Qaeda in 2016. When he became the head of HTS in 2017, he appeared to adopt ationalism and distance himself from an uncompromising militant jihadist ideology.
On January 29, 2025, Al-Julani — under his real name, Ahmad al-Sharaa — was inaugurated as Syria’s interim president. While Israel remains wary of his origins, Western nations have cautiously welcomed him. The author wishes to watch with hope as Syria embarks on its rebirth.
1. The Assad Regime’s Negative Legacy and the Fight Against IS
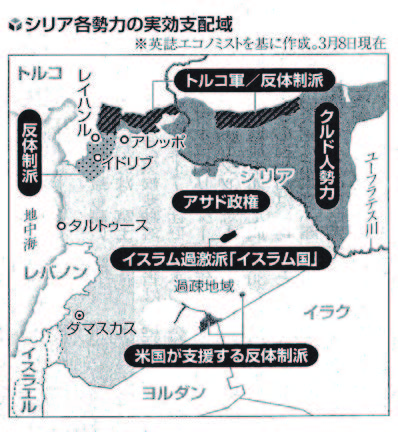
The map below, published in The Yomiuri Shimbun in March 2021, shows the territorial control of various factions in Syria. The nation was roughly divided into four regions of control (For details, refer to the News Report Summer 2021 issue, “Syria Today: Ten Years After the Arab Spring, Still in a State of Civil War.”)
① Assad regime territory—shown in light gray, centered around Damascus, covering about 60% of Syria.
② Remaining IS territory—the white area in the east, spasely populated and extending toward Iraq and Jordan, containing U.S.-controlling the Iraqi border.
③ The Free Syrian Army, trained by Western and Turkish forces, held the western side of the Euphrates River, while the U.S.-backed Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF) controlled the east after defeating IS. Turkey later expelled certain factions PKK(Kurdistan labor party), consolidating Kurdish dominance, and placed the “safe zone” under Turkish military police supervision.
④ Idlib Province—the dark gray, dotted area controlled by the opposition.
HTS, which now leads the country, originally ruled over ④Idlib. Although once labeled a militant group, HTS had already severed ties with IS in 2014 and declared its break from al-Qaeda in 2016 —not due to mere tactical differences, but because of Islamic ideological divergence. HTS sought to establish a national salvation government grounded in Syrian nationalism, in contrast to IS or al-Qaeda’s militant jihadism, which aimed for an intolerant, isolationist Islamist state.
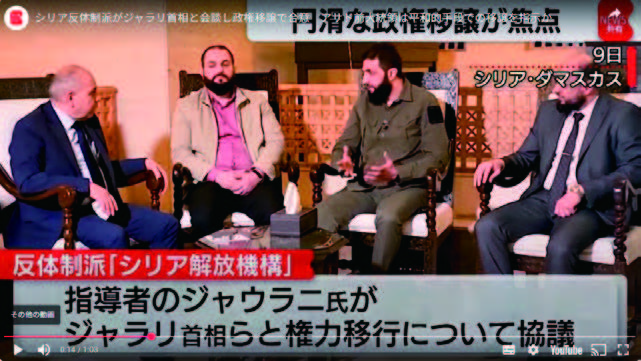
‘HTS leader Al-Julani meets with former Prime Minister AlJalali and agrees on the power transfer.'(Screenshot from TV Tokyo Biz YouTube, Dec. 10, 2024.)

Muhammad Bashir, head of the Syrian Salvation Government, Idlib, Nov. 28, 2024. AFP/Jiji Press, Dec. 10,2024.
2. Interim President Al-Sharaa Meets Turkish President Erdoğan

Interim President Al-Sharaa and President Erdoan discuss the Kurdish issue, Feb. 5, 2025. (Screenshot from ANNnewsCH YouTube channel.)
One of the new government’s toughest challenges lies along its northern border with Turkey and within the Kurdish territories surrounding the Euphrates River—regions that had become quasi-autonomous during the civil war.
For the new administration, the Kurdish forces were difficult partners: though they shared opposition to Assad and fought IS alongside the United States, they had no political alignment with the new leadership, nor similar political groups.
Turkey, which had refused to support Assad, welcomed Al-Sharaa’s firm position that “Syria must be a nation where all citizens can coexist, and weapons must not exist outside the state’s control”. His government maintained a policy of disarmament and the integration of all militias into the national army.
Crucially, Al-Sharaa accepted Turkey’s long-standing demand that the YPG (People’s Protection Units)—the core of the SDF—be dismantled.
President Erdoğan personally sent his presidential aircraft to receive Al-Sharaa in Ankara. The two leaders reportedly agreed that “Syria and Turkey will cooperate in the fight against IS in the Kurdish-controlled northeast”. Erdoğan also pledged to support efforts to lift Western sanctions on Syria.
Soon after, the Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF) formally merged with the Syrian interim government. The agreement was signed on March 10, and Erdoğan welcomed it, stating that it would “contribute to the region’s security and stability”.
3. Interim President Al-Sharaa Meets U.S. President Trump—Sanctions Lifted

May 14 , President Donald Trump meets Syria interim President Ahmad Al-Sharaa in Riyadh. (Screenshot from Al Arabiya News.)

President Trump warmly welcomes Al-Sharaa before their talks.
Although the non-disclosure meeting between President Donald Trump and Interim President Al-Sharaa lasted only thirty minutes, it was a momentous opportunity for Syria to embark on its reconstruction as a new nation. From May 13=15, President Trump toured Saudi Arabia, Qatar, and the UAE, and the highlight was his surprise meeting with Al-Sharaa. During the talks, Trump declared: “To give Syria a new start, the United States will lift its sanctions”.

From The Wall Street Journal
The news sparked jubilant celebrations in Damascus, where crowds gathered in Omayyad Square on the evening of May 13, setting off fireworks in joy.
The lifting of sanctions was not unconditional.
The details of the non-disclosure meeting between President Trump and Mr. Sharaa have not been disclosed, but the lifting of sanctions was not unconditional.According to a White House spokesperson, the U.S. decision came with conditions: all foreign terrorist fighters must withdraw from Syria; Syria must recognize Israel diplomatically; and Syria must cooperate with the U.S. to prevent the resurgence of IS.
Even though the summit was off-record—the first such meeting in twenty-five years—it is clear that President Trump offered Syria a new beginning and urged GCC and Western nations to accept Al-Sharaa as a legitimate leader
4. Syria’s Pending Issues—The Golan Heights and the Druze Question
For Syria, normalization with Israel will hinge on resolving two sensitive issues: security in the Golan Heights and the status of the Druze population in Sweida.
The Golan Heights Issue
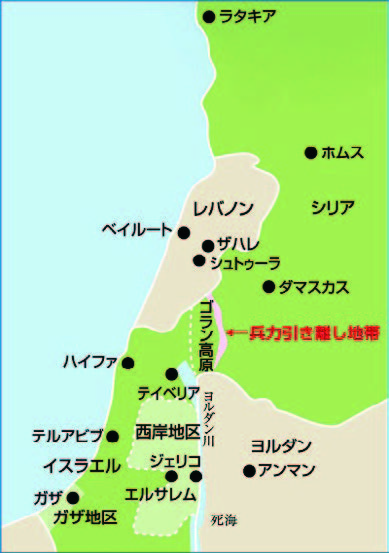
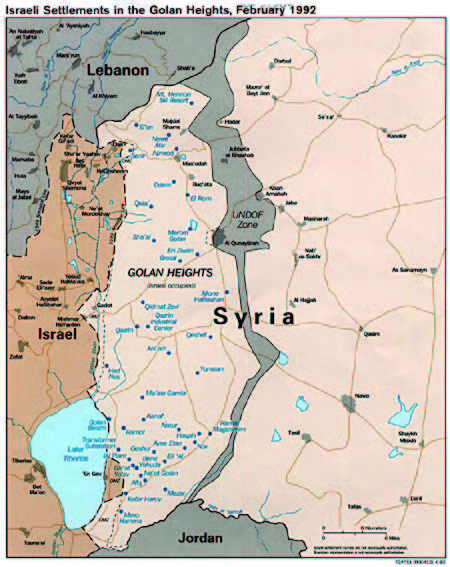
The map on the upper left and the italicized description below are excerpts from the official website of the Secretariat of the International Peace Cooperation Headquarters, Cabinet Office. The map on the right is based on the 1992 Golan Heights map (from Wikipedia).
The Golan Heights is a rocky plateau in southwestern Syria that overlooks the Jordan River basin. Its location makes it strategically important not only for military reasons but also for securing vital water resources. Israel captured the area during the Six-Day War in 1967, and although Syria briefly regained control during the Yom Kippur War in 1973, Israel soon reoccupied it. Tensions in the region remain high today. In 1974, after Syria and Israel reached an agreement to disengage their forces, the United Nations established the United Nations Disengagement Observer Force (UNDOF) to monitor the ceasefire and oversee the separation of troops between the two sides.
The situation has persisted for fifty years because, although UN Resolution 242 called for Israel’s withdrawal, Israel refused to comply, arguing that the resolution did not guarantee its right to live in peace within secure and recognized borders. On May 1, 1968, Israel agreed to accept the resolution on the condition that its right to exist as a state be recognized — a principle later known as “land for peace.” From October 6 to 24, 1973, the Fourth Middle East War—fought between Egypt and Syria on one side and Israel on the other—took place. As a result, Egypt failed to regain the Sinai Peninsula, and Syria was unable to recapture the Golan Heights. Subsequently, the famous Camp David Accords of September 1978 — a reconciliation between Israeli Prime Minister Menachem Begin and Egyptian President Anwar Sadat — led Israel to return the Sinai Peninsula to Egypt. The principle of “land for peace” was thus put into practice. Syria, however, under the Ba’athist Assad regime, never pursued a similar peace treaty. Thus, Israel and Syria have remained technically at war, with no diplomatic relations since 1974.
Al-Sharaa has declared his intention to build a democratic, cooperative, and moderate Syria, neither a leftist authoritarian state nor an Islamist theocracy. Whether this vision is genuine depends on whether he will recognize Israel as a state—a prerequisite for resolving the Golan Heights issue.
The Druze and Sweida Question
The Sweida problem is closely tied to the Druze minority, numbering about 1.5 million across Israel, Syria, Jordan, and Lebanon. The Druze follow a secretive offshoot of Islam, prohibit intermarriage with outsiders, and pledge loyalty to the governments of their residential countries. In Israel, Druze citizens fought for independence and serve in the Israeli army ; in Syria, they traditionally served loyally under Assad.
In 2015, the Druze massacre in Syria occurred when anti-Assad Nusra Front fighters killed Druze loyal to the regime. The group later apologized, citing a command error. Recently, clashes between Druze and other tribes in Sweida led to Syrian government troop deployments, reportedly after Druze leaders sought Israeli protection through kin across the border. This triggered Israeli involvement and subsequent escalation.
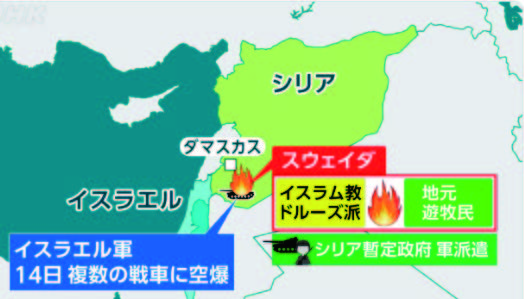
NHK World, July 18, 2025:“ The Intent Behind Israel’s Airstrikes in Syria.”
Archives
1. Aug. 2025 The Trump Administration and the Situation in the Middle East―Iran is weakening and complicating the regional order
1. May. 2025 Will peace in the Middle East progress with the Trump administration?
1. Feb. 2025 The Path of Construction that Begins with Overcoming the ‘War on Terrorism’ (Part 2)
1. Nov. 2024 The Path of Construction that Begins with Overcoming the ‘War on Terrorism’ (Part 1)
1. Aug. 2024 Kuwait seeks true peace
1. May. 2024 Sanriku Railway Forms Ties with Kuwait
1. Feb. 2024 Anti-Semitism fueled by radical Islam and leftist ideology
1. Oct. 2023 Massive “Hamas” Terrorism Not Good for Palestine
1. Aug. 2023 Approval of the UK’s TPP Membership and Six Eyes
1. May. 2023 Saudi-led Arab countries
1. Feb. 2023 Japan Earns Trust as a Peaceful Nation
1. Nov. 2022 Gulf States and Israel Looking for Peace
1. Aug. 2022 Former Prime MinisterShinzo Abe, who made Japan credible as a global peaceful nation.
1. May. 2022 Warfare in the New Era:Digital Strategies as Deterrence Enhancement
11. Feb. 2022 Deepening and Expanding the Japan-US Alliance is the Way to Overcome China’s Communist
11. Nov. 2021 Free and Open Indo-Pacific Initiative and Afghan Problems
11. Aug. 2021 Peace in the Middle East and Japan: On the Occasion of the 30th Anniversary of the Gulf War
11. May. 2021 “Free and Open Indo-Pacific” for which global support is expanding
11. Feb. 2021 Thorium Molten Salt Reactors That Open the Gate of the Second Atomic Energy Age
11. Nov. 2020 Seriousness of Pompeo’s View on China and Subsequent Policy
11. Aug. 2020 Japan to set sail for full-scale peace diplomacy to the Middle East (3)
11. May. 2020 Japan to set sail for full-scale peace diplomacy to the Middle East (2)
11. Mar. 2020 Japan to set sail for full-scale peace diplomacy to the Middle East (1)
11. Nov. 2019 e-sports featured as a cultural project in the National Sports Festival
11. Aug. 2019 Status of Crude Oil Prices
11. May. 2019 Polygamy debate in Egypt: Statement of Ahmed el-Tayeb, Grand Imam of al-Azhar, supreme authority of Sunni
11. Feb. 2019 Year 2018 turned out to be the first year of e-sports
11. Nov. 2018 Trends in world economy and crude oil price in a Goldilocks economy
11. Aug. 2018 Full-scale launch of the plan to make programming education for e.s. compulsory by 2020
11. May 2018 President el-Sisi’s achievements over the past four years and prospects for the next four years
11. Feb. 2018 ESports getting prevalent in the Middle East ― To be an official athletic event from 2022 Asian Games
11. Aug. 2017 Aggressiveness of Islam and Imam’s anti-terrorism declaration
11. May 2017 Countdown to the destruction of the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS)
11. Feb. 2017 Trump administration’s policy toward the Middle East
11. Nov. 2016 25 years after the end of Gulf – “Meeting of supreme Islamic leaders”
11. Aug. 2016 Announcement of the construction plan of the bridge between Saudi Arabia and Egypt across the Red Sea
11. May 2016 Deepened international collaboration for destruction of ISIL: Desired outcome of G7 Summit
11. Feb. 2016 Saudi Arabia vs Iran, Crucial moment
11. Aug. 2015 The results of international encirclement against the militant group, the Islamic State and the future challenges
11. May 2015 The GCC DAYS IN JAPAN held in Tokyo April 22-24, 2015
11. Feb. 2015 The limitation of the Arab Spring ― Egypt and Tunisia after the Arab Spring
11. Nov. 2014 3 Months from the Islamic State Shock – Change of US Strategy for Air-Strikes and Encirclement
11. Aug. 2014 High expectation for Egypt’s el-Sisi administration’s efforts in mediating ceasefire
11. May 2014 Kuwait’s enthusiastic assistance for recovery from Great East Japan Earthquakes
11. Feb. 2014 Roadmap to Democratization of Egypt
11. Nov. 2013 Era in which “Live Healthy” is contribution to the society
11. Aug. 2013 Public speech of Ms. Sara Akbar
11. May 2013 Merits and demerits of the US-Iraq War
11. Feb. 2013 Expectation for Prime Minister Abe to implement the best energy policy
