Trends in world economy and crude oil price in a Goldilocks economy
– Looking back over 10 years from the Lehman shock –
Investment analyst Kuniharu Watanabe
From the Winter Issue of the electronic “Salaam Quarterly Bulletin”, No.27, November 2018
Ten years have transpired on September 15 since the Lehman shock which Mr. Greenspan, former Federal Reserve Chairman Mr. Greenspan, described as an event which can occurs only once in 100 years. Once again, looking back on what was the Lehman shock, what triggered it was a subprime loan problem that had emerged in the market since around 2007. A subprime loan is a loan made to people with low creditworthiness such as low-income people against the backdrop of the housing boom in the United States. While house prices were rising, loan losses did not occur much, but as the rise in housing prices ceased and interest rates rose, the cases of inability to repay the debt increased. Furthermore, the problem was not limited to that, and securitized subprime loans and Collateralized Debt Obligations (CDOs) referencing these loans were sold all over the world. The management crisis of the large US housing finance companies has surfaced in March, 2007.
After that, the financial institution hedge fund experienced losses of huge amount one after another and, due to the collapse of Lehman Brothers on September 15, 2008, the impact spread globally, causing the global financial crisis. The market liquidity disappeared, stock prices in the world crashed, and the unemployment rate in the United States deteriorated to 10% at a stretch and the wave of depression swallowed all over the world.
Utilizing the past experience of the Great Depression, the United States prompted the world to respond

Mr. Ben Bernanke.
An American economist, specializing macroeconomics.
14th Chairman of the Federal Reserve System.
It was said once in 100 years, and 100 years date back to the 1929 Great Depression. At that time, the United States adopted measures such as New Deal policy, but each country resorted to protectionist trade for defense of their own, the world economy shrank, and the global recession prolonged, eventually leading to the World War II.
In the case of the Lehman shock, researches, knowledge and experiences accumulated over 100 years were mobilized and quick response was made from the time of occurrence. In particular, the urgent and drastic rate cuts by the US Federal Reserve Board, chaired by Mr. Bernanke, and the so-called QE implemented three times, were unprecedented policies in the human history and experiments. Politically G20 was established, and each country cooperated with policies such as fiscal spending, and achieved economic recovery to this day.
“Quantitative Easing” that led the recovery
First of all, one of the biggest factors that led the recovery from the Lehman shock was QE (Quantitative Easing) implemented by the US Federal Reserve three times as already pointed out. At that time, the FRB chairman was Mr. Bernanke who took over from former Chairman Greenspan in 2002. He was an economist and his specialty was the collapse of Japan’s bubble economy. Because of his remark that it is good to spread money from helicopter in order to get out of a serious deflationary economy, he has a nickname of Helicopter Ben. QE carried out three times was an application of his own research results and implemented a zero interest rate immediately after the Lehman shock. In short, QE is a policy to increase the amount of money circulating in the market.
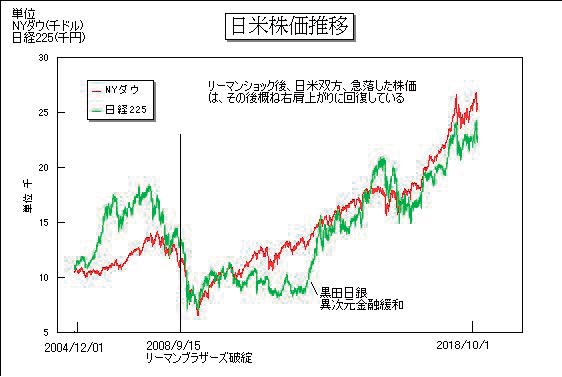
US, Japan Stock Price Trend:unit;NY Dow (thousand dollars), Nikkei 225 (thousand yen)
Graph:red; NY Dow, green; Nikkei 225
After the collapse of Lehman Brothers on September 15th in 2008, the plunged stock price of both Japan and the United States has recovered and continued rising.
As a result, the stock price has continued to rise for the next 10 years. In his speech at Jackson Hall in 2012, Mr. Bernanke mentioned a word about tapering (reduction of quantitative easing) and the stock price worldwide fell sharply from the next day. This showed that the recovery of the stock price was totally dependent on FRB’s monetary easing. Since this incident, the Fed will take a very cautious stance on the start of rate hike and its pace.
Japan’s lost 20 years and Lehman shock
Initially, the impact on Japan was thought to be limited. The reason is as follows. Regarding the subprime loan problem that triggered the Lehman shock, Japan experienced the financial crisis such as the collapse of the bubble in 1990, the failure of Yamaichi Securities in 1997. Japan was in the midst of the lost 20 years, and people disliked taking excessive risks and restrained investment related to subprime loans.
However, as the world economy fell into recession and the yen appreciated rapidly, Japan suffered a serious recession due to influence from these. Stock prices fell to 7054 yen which was the lowest price since the collapse of the bubble and the yen appreciated from 110 yen to 87 yen to the dollar. After that, during the Great East Japan Earthquake the dollar value to the yen fell to the lowest post-war level which was 75.54 yen. Many companies went bankrupt, large-scale restructuring and dispatch cuts were made, and many people lost their jobs.
Current situation in Japan that cannot find an exit

Bank of Japan led by Mr. Kuroda monetary easing in different dimensions.
Since the collapse of the bubble economy, Japan’s economy has continued to stagnate for 20 year as the period is called the lost 20 years. Meanwhile, it is Japan that pioneered non-traditional policies such as zero interest rate policy and quantitative easing before the United States. However, Mr. Bernanke criticized the Bank of Japan’s policy as incomplete. Some intellectuals pointed out that they should take bolder monetary easing. However, the Bank of Japan ceased a zero interest rate before coming out of deflation, betraying the expectations of the market, and never stepped into any further bold monetary easing. At the same time as the establishment of the second Abe administration, Mr. Kuroda took office as the Bank of Japan President and launched monetary easing in different dimensions.
By doing so, he induced the first full-fledged yen depreciation after the bubble burst. However, the 2% price increase target set by the Bank of Japan is still far away, and currently only the Bank of Japan cannot see the exit at all, while the United States, followed by the ECB and other countries’ central banks trying to move towards the exit. The Bank of Japan holds a large amount of government bonds and a large amount of stocks which is distorting the market principle and paralyzing a market function.
A Goldilocks economy and “Exit strategy” sought after
The present world economy is called a Goldilocks economy. It means a moderate economic growth under conditions of low interest rate and low inflation. If you do notice it, it is said that the stock price in the United States continues to update the highest stock price in history, the US employment statistics released every month also continue positive trends and is said to be close to full employment.
Many countries such as ECB followed the example of the United States, lowered interest rates and, in some cases, carried out palliative monetary policy such as large-scale purchase of government bonds similar to QE. As of today, there are only a few countries that are in the stage of full-scale interest rate hike like the United States, and they are looking for the best timing of moving towards “exit”.
In other words, it can be said that the mankind have overcome the unprecedented economic crisis by gathering wisdom. However, as anomalous low interest rates and palliative monetary policy prolong, the economic recovery backed up by it has caused various adverse effects and distortions. There are concerns that these may surface as the next crisis. The central banks in each country are seeking “exit strategies”, and that means they have not come out of the exit completely.
Inauguration of G20 and fiscal stimulus in China
Along with monetary policy of central banks, inauguration of G20 cannot be overlooked. The Bush administration expanded the existing G7 framework to include emerging countries such as China, saying that the conventional G7 framework alone could not cope with the unprecedented crisis.
Although some people questioned whether unified opinions and policies could be adopted among 20 countries, it can be said that the attitude to cooperate and solve problems multilaterally was effective. In that framework, China announced that it will make a large fiscal stimulus of 4 trillion yuan. This is the second factor after the FRB’s QE.
It is a fact that the world economy was supported by this. As a result of this, China deepened her self-confidence and become the world’s second largest economy and at the same time showed its behavior as a major power. It strengthened influence to other countries with the One Belt One Road Initiative and tried to build a world order centered on herself in challenge against the United States. Authoritarian Xi Jinping regime is also not unrelated to these developments. However, on the other hand, due to the capital investment made under unrestricted spending policy at that time, China has numerous problems such as excessive production capacity of steel and nonperforming loans.
Challenges to globalism for global symbiosis
Britain decided to break away from the euro zone by a referendum. Negotiations encounter difficulties even now as the agreement deadline with the euro zone for withdrawal approaches. Uncontracted withdrawal or disorderly withdrawal is taking on reality. Politicians with nationalistic assertions are gaining popularity in the euro zone countries, and anxiety persists that a country may decide to depart from the euro zone at any time.
In the United States President Trump who advocates America First was inaugurated. His unilateral methods to use the United States’ military power and economic power to demand concessions from allies as if he is dealing with enemies are causing anxiety and repulsion among other countries.
It seems that these are resistance to hasty globalism, but is it a temporary thing? Or perhaps the tidal current so far is completely refluxed, and converted to nationalism? The world is now at a big crossroads, and is urged to choose a big theme.
The stock market crash in 1929 caused the economic depression to worsen and resulted in seriousness and prolongation as central banks, who were optimistic about the recovery trend in 1937, started raising interest rates. And, as each country adopted a protectionist trade policy to protect their economy, the global economy was driven to stagnation and shrinkage. Eventually it concluded in the form of war, but the way to nationalism is likely to repeat a past mistake.
The economy does not develop where freedom and trust are absent. A large-scale investment is not possible in unstable and unpredictable society that does not know how the social system will change tomorrow. A large-scale investment will take place and the economy can develop greatly when it is believed that systems with services, money freely flowing through the national barrier will last for a long time. And that is the way the world can coexist. In the haste of globalism, the distortion needs to be rectified, but globalism itself should never be denied.
Determination of crude oil price through quantitative easing (QE) and collaborative production reduction
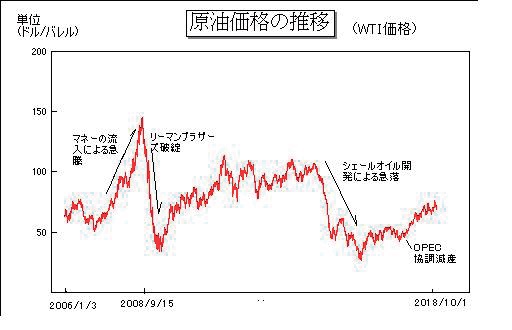
Change of crude oil price (WTI price) : Unit (dollar / barrel)
Explanation in the graph : from left, Soaring due to the infusion of money, Lehman Brothers collapse,
Plummet caused by shale oil development, Collaborative production reduction by OPEC
Monetary relaxation was implemented before and after the Lehman shock, and the destination to which a large amount of money supplied to the market moved was the commodity market. The crude oil price reached the market maximum of 147 dollars. After that, crude oil prices also dropped dramatically to 27 dollars as investors tried to avert risks in all markets including stock and foreign exchange markets. Although it subsequently recovered to exceed 100 dollars, the price dropped dramatically to 27 dollars again due to the fear of excessive supply caused by the development of shale technology. Currently, it has recovered to more than 70 dollars and has been stable in general.
Cooperative production reduction by OPEC is supporting current recovery and stabilization of crude oil price. Non-OPEC countries such as Russia are also involved and these are being implemented. Some of them are politically and religiously antagonistic to each other, but they are coordinating to stabilize crude oil prices.
At present, the crude oil price is at the highest value after the plummeting of the price due to increase production of shale oil. The reason behind is the withdrawal of the United States from Iran’s nuclear agreement and the reactivation of sanctions. It is anxiety about supply due to the reduction of supply from Iran caused by sanctions against Iran.
Regarding crude oil price, the interests and speculations of each country intersect. Through the framework of multilateral cooperation, including OPEC, interests of each country can be adjusted, and various problems can be solved. When that framework is removed and the balance between demand and supply collapses, crude oil prices may run out of control in upwards or downwards either way.
Summary
It seems that the economy has recovered steadily for ten years since the Lehman shock. However, it still contains various distortions and harm caused in the process of recovery, and the present world economy is sustained on the subtle balance in reality.
The fact that a big tide of the era that has continued since the end of the war is going to change should not be overllooked.
From now on, it is necessary to pay attention to where the world is going.
More contents available in the electronic “Salaam Quarterly Bulletin”, No.27, November 2018.
