Full-scale launch of the plan to make programming education compulsory for elementary school by 2020
Tominari Sano, Journalist
From the Autumn Issue of the electronic “Salaam Quarterly Bulletin”, No.26, August 2018
In the new education guidelines for elementary schools to be implemented from fiscal year 2020, “programming education” for nurturing logical thinking skills is made compulsory, and subsequently it is planned to be gradually expanded to junior high schools and high schools. However, about 40% of parents of elementary, junior high and high school students answer “I do not know” about the plan to make “programming education” compulsory. Meanwhile, the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry forecasts that the shortage of IT human resources will expand to as many as 790,000 people by 2030. How can we overcome the current situation where changes in skills required by the society and changes in policies on learning are not sufficiently publicized?
Estimated supply and demand of IT human resources
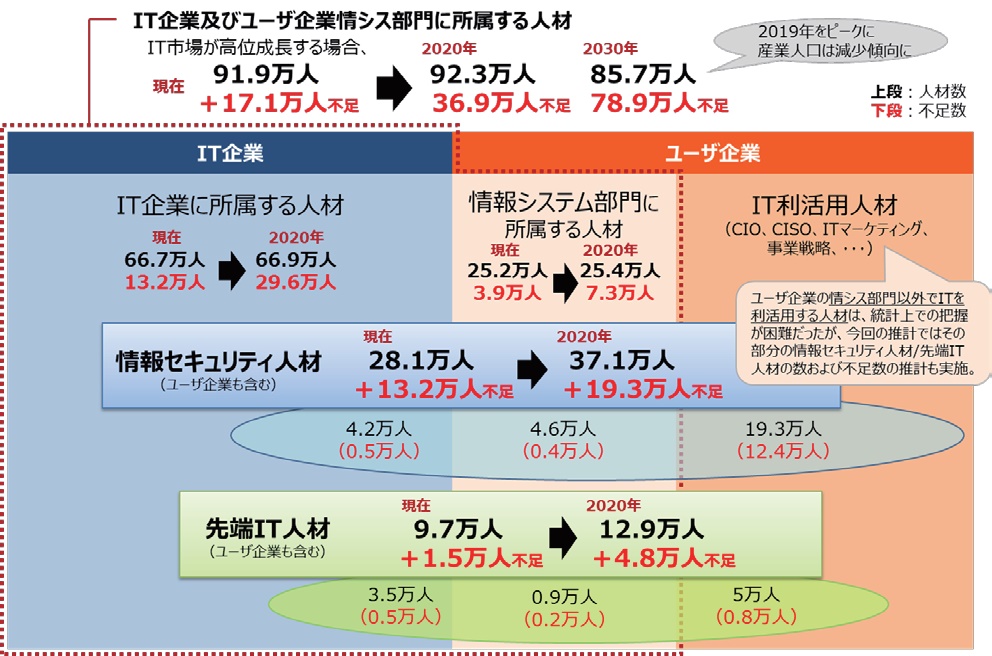
· The Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry conducted questionnaire surveys and research groups by experts on IT human resources expected to play an important role in the growth of Japanese industries in the future, and the trend of human resources supply and demand in the medium to long term and the future measures for securing and nurturing of IT human resources were examined.
· In the main report, estimates are made on the growth rate of the IT market and the expected improvement in productivity by different scenarios.
· The number of information security talents is currently about 280,000 and the shortage is about 130,000, but in 2020 the number of shortages has expanded to less than 200,000.
[From the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry website “Estimate on Supply and Demand of IT Human Resources” (both reference diagram and chart quoted with explanatory text)
http://www.meti.go.jp/press/2016/06/20160610002/20160610002.html – 2018-01-20]
Programming Education

TEPIA (Association for Technological Excellence Promoting Innovative Advances) Robot programming · 3D printer classroom image
Although it is called “programming”, it includes various items such as electric engineering (robot making, artificial intelligence development like AI), entertainment (e.g. game programming), and anti-virus measures indispensable in the IT era. The government considers “developing and securing high-level IT human resources that will be the source of industrial competitiveness” as a growth strategy, and intends “to acquire 21st century-type skills using IT” and implement “clarification and utilization of skill level of human resources”.
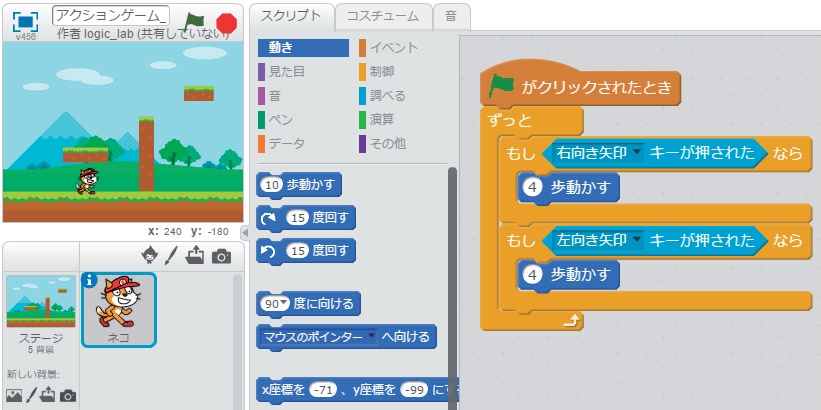
Scratch (programming language learning environment developed by MIT Media Lab) is a learning site that facilitates students to acquire programming skills
“What is the thing that determines the competitiveness of our country? It is IT power. In Europe, IT power is recognized as an indispensable element for young people to enter the labor market, and many countries and regions are introducing programming as part of the curriculum of the school education, “explains the government as background. In the United States which is advanced in IT, NPO organizations with the support of Bill Gates and Mark Zuckerberg are engaged in activities to introduce programming classes at schools throughout the country. UK makes programming education compulsory for all children from 5 to 16 years old. South Korea decided to make programming education compulsory at elementary schools since 2017.
Aim and task for mandatory programming education

Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications, and Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry cooperated to prepare preparation summary entitled “Towards Making Elementary School Programming Education Mandatory” and introduced that preparation for programming educational implementation at elementary school stage was completed.
According to a survey by the Cabinet Office, the PC penetration rate and ownership rate in Europe and the United States are 60 to 70% among junior high school students, but about 20% in Japan which is very low. Although the spread of smartphones has reached 55 million people, we cannot overlook the fact that people who cannot use PCs are increasing. Therefore, dissemination of IT tools left to the needs of the citizens does not necessarily lead to improvement of IT capabilities.
It is stated that the aim of compulsory programming education at elementary schools is “to nurture programming thinking, to encourage realization that the information society is supported by information technology such as computers, and to nurture attitude to solve familiar problems by utilizing computer and build a better society.” Simply put, it is familiar to IT tools, “Learning logical thinking” and does not do professional programming. In other words, for elementary school students, instead of educating programming knowledge, it is a simple education to teach students to move things by combining basic programs of moving an object forward and backward to front, back, left, and right using programs already installed. It aims at having children get interested and to have them experience the enjoyment of making things by programming.

Individual farmers develop a “cucumber sorting machine”.
In schools, equipment based on tablets has already been distributed. Children are already familiar with handling of smartphones, and some children can use PC tools well. However, many children are accustomed to moving things with fingers on tablets and smartphones rather than PCs. On the other hand, there are children who learn them for the first time at elementary schools. Also, due to the spread of smartphones, students who cannot use PCs start working in the society, and face difficulties as they have to use PCs for the first time when they enter a company. This kind of problem is happening in reality. It is one of challenges to fill the gap such as this.
Book on Programming Elementary and Junior High School Students Can Start

2018 edition of the “Book on Programming Elementary and Junior High School Students Can Start” was published by Nikkei Business Publications, Inc. The way to read this book is written next to the table of contents, and icons are attached in each chapter so that one can distinguish the article for elementary and junior high school students, the article for high school students or the article for parents. The first chapter has an article for parents titled “What Parents Should Know First” which poses four questions to parents. They are interesting questions so let me introduce them here.
“If elementary and junior high school students do programing, there will be benefits in the future. What are they?”
One can choose one of 4 options: ① Become a programmer, create a game wildly popular and earn a lot of money; ② Prepare for compulsory programming education of (elementary school) starting in 2020; ③ Because shortage of IT human resources is expected in the future, one does not have any difficulty finding employment; ④ The possibility of becoming a person who can lead the world in the future will increase. The correct answer is of ④. Of course, ①, ②, ③ are not mistakes either. But it is stated that the biggest reason for the current programming boom is ④ and the reason is explained (omitted here).
Survey on consciousness about the future that junior high and high school students envision conducted on April 25, 2017
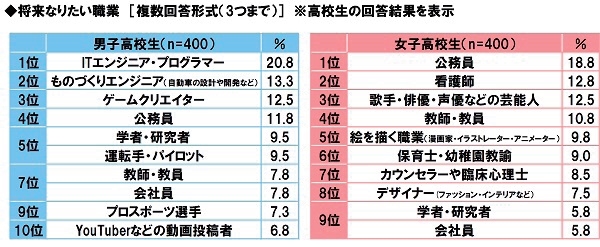
Footnote below) For high school students, in case of jobs desired by male high school students, the job ranked first was “IT engineer, programmer” (20.8%), second place “manufacturing engineer (automobile design and development)” (13.3%), third place “game creator” (12.5% ), 4th place “civil servants” (11.8%), 5th place “scholar, researcher” and “operator, pilot” (both 9.5%). In case of female high school students, the job ranked first was “civil servant” (18.8%), second place “nurse: (12.8%), 3rd place “Entertainers such as singer, actress, voice actress” (12.5%), 4th place “teacher and educator” (10.8%), 5th place “visual artist (cartoonist, illustrator, animator) “(9.8%). Civil servants and nurses seem to be a popular occupation for female high school students.
[The above table and explanation are from the Internet research results of Sony Life Insurance Co., Ltd. consciousness survey on the future envisioned by junior high and high school students conducted nationwide from March 21 to March 27, 2017. It is based on the total number of valid samples of 1,000 people (200 junior high school students and 800 high school students).]
In the fifth chapter of this magazine, there is an interview article on “What should parents do for compulsory programming education” under the title “Before Going to Programming Classroom”, as well as a guide on over 50 programming classrooms throughout Japan.
I covered the “Programming Kids” school for students from first grade to 12th grade, which is introduced as one of them.
Programming Kids
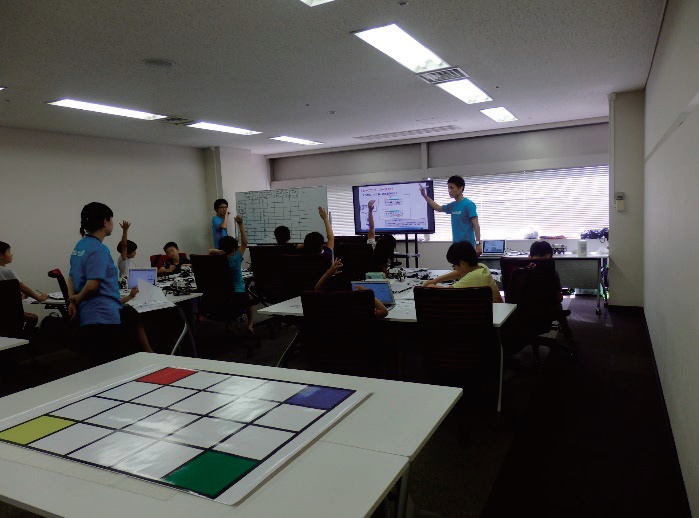
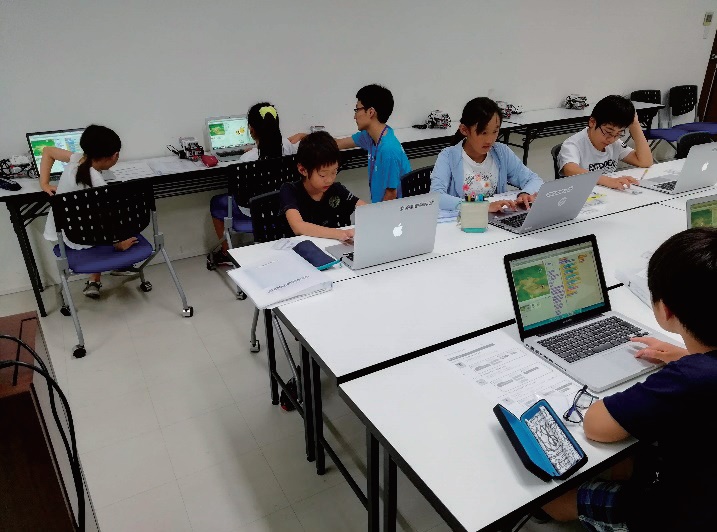


Classroom scene of Programming Kids classroom (Mizonokuchi school)
“Kanagawa Science Park (KSP)” (Kawasaki city, Kanagawa prefecture) is located at the place which is 5 minutes by bus from Mizonokuchi Station on JR Nanbu Line and Musashi Mizonokuchi Station on Tokyu Denen Toshi Line. When I visited there on June 30, a programming class attended by elementary school students was held at a corner of the Park.
The classroom sponsored by Number One Solutions Co., Ltd. (Headquarters: Meguro-ku, Tokyo) is held in Ikejiri Ohashi (Meguro Ward), Futago Tamagawa (Setagaya Ward), Saginuma (Kawasaki City) in addition to Mizonokuchi. At Ikejiri Ohashi site, classrooms are held for junior high and high school students. Mizonokuchi school has classes for elementary school 2nd grade students (basic course) from 10:00 to 12:00 and for 3rd to 6th grade students (advanced course) from 13:00 to 15:00 on 1st and 3rd Saturday. Each classroom has ten students.
Programming fun for kids
I went to see an advanced course for the third grade students. It is not an advanced program education. It provides children with opportunity to become interested in programming and observe the process through which they overcome challenges. As to a process of teaching, software such as LEGO ® Mindstorm ® EV 3 and Scratch, Viscuit, etc. are used as teaching materials, and a unique curriculum for the classroom was prepared. This curriculum is the know-how of the Programming Kids classroom. Features of the curriculum are to allow students themselves to have a pleasant experience through the process to find a solution to the problem by trial and error. Classroom instructor, Mr. Horiuchi said, “While making trial and error, considering and advancing solutions is essential for programming. That is what I believe.”
Indeed, while the classroom has an atmosphere like the school classroom scenery, the children seriously listen to the instructor’s words. They immediately answer the instructor’s question and act according to the instruction. 2 hour learning time is divided into segments of 10 minutes, 40 minutes, 10 minutes break, 40 minutes, 15 minutes, and 5 minutes, and flows without waste.
Class flow
In the class I observed, the instructor taught children the basic technology of how to do the work of moving a prepared car, through animated character images created by the classroom.

In the second half of the classroom lesson, children tries to actually move a car by using the knowledge gained in the first half.
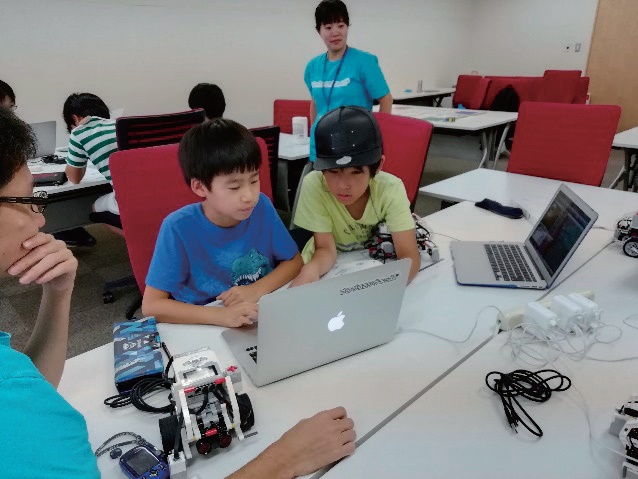

After all, the children were more lively in tackling with the work to move the car in the latter half than the first half of the class. The work was to clear some problems such as moving the car straight ahead, making left turn, right turn, moving it diagonally, backward and ultimately reaching a goal.

A child with a smile who cleared the task at first attempt

Some children cleared the challenge at once, while others have gotten the instructor’s OK and smiled while going back and forth between their seats and the instructor’s twice or three times. The staff coordinated on the spot when a child said “Why the car does not move well?” If that does not solve it, the child returned to his seat and reconfirmed. However, there is also happening that it does not go as programmed. Still, it is a pleasant scene to observe that children trying to solve the problem without being impatient.
At the end of the lesson, efforts were made to keep children’s interests, such as “reviewing” and scoring each challenging issue.
Number One Solutions Co., Ltd.
Mr. Susumu Hashimoto, Executive Managing Director of Number One Solutions Co., Ltd. said, “20% of the children have their own PC. I lend it to children who do not have it.” Although it is slight difference between a child who owns PC and a child who does not, it is not big difference. On the other hand, as an ingenious device to generate children’s interests, by making steady efforts such as “to keep important points and to make them abstract”, “to score comments and questions to encourage children to express a lot of opinions”, children can enjoy learning. It was impressive that many of the attending children on this day were raising their hands.
Mr. Hashimoto said, “I would like to value things that are not just skills,” as he emphasized that he would like to value not simply pursuing skills, but the process in leading up to gaining skills.
Vision “To realize world peace through technology”

Tetsuo Omonari, Representative Director, Number One Solutions Co., Ltd.
Mr. Tetsuo Omorai, President of Number One Solutions Co., Ltd., expressed his ambition, by saying, “I gained confidence that programming education can nurture the ability to survive the 21st century. Through Programming Kids and other programming classes, I want to nurture engineers relevant to the industry and human resources who create programs on my own.” In addition, he sets forward a vision “to realize world peace through technology” and demonstrated his conviction that since the introduction package for programming education has already been prepared the unique educational style of Number One Solutions can also be expanded abroad.
I hope that programming education of Number One Solutions can be introduced to Middle Eastern countries as a new education industry and a peace industry, as Middle Eastern countries including Egypt and Saudi Arabia are currently turning their eager eyes on Japan’s educational style.
Footnote) [Translation of the table]
Desired future jobs (up to 3 items can be selected) *High school students’ responses are shown
Male high school students (n=400)
1. IT engineer, programmer: 20.8%
2. Manufacturing engineer (such as automobile design and development): 13.3%
3. Game creator: 12.5%
4. Civil servants: 11.8%
5. Scholar, researcher: 9.5%
5. Operator, pilot: 9.5%
7. Teacher, educator: 7.8%
7. Company employee: 7.8%
9. Professional athlete: 7.3%
10. Contributor of videos such as YouTuber: 6.8%
Female high school students (n=400)
1. Civil servants 18.8%
2. Nurse 12.8%
3. Entertainer such as singer, actress and voice actress 12.5%
4. Teacher, educator 10.8%
5. Visual artist (cartoonist, illustrator, animator) 9.8%
6. Day care and kindergarten teacher 9.0%
7. Counselor or clinical psychologist 8.5%
8. Designer (fashion, interior) 7.5%
9. Scholar, researcher 5.8%
9. Company employee 5.8%
More contents available in the electronic “Salaam Quarterly Bulletin”, No.26, August 2018.
